When it comes to the muscles of the forearm, the flexor digitorum superficialis often gets overlooked, much like that one friend who always shows up late to dinner. But this muscle plays a crucial role in hand function, allowing for those elegant finger movements we take for granted. Understanding its origin and insertion might not win you any trivia nights, but it’ll definitely make you the go-to expert at your next anatomy discussion.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Flexor digitorum superficialis serves as a key muscle in the forearm, contributing significantly to finger flexion. This muscle originates from the common flexor tendon located at the medial epicondyle of the humerus, as well as from the ulna and radius. Specific points of origin include the coronoid process of the ulna and the anterior surface of the radius.
Insertion occurs at the middle phalanges of the second to fifth digits. This unique positioning allows the muscle to flex the proximal interphalangeal joints effectively, demonstrating its essential role in hand function. It can be observed that the flexor digitorum superficialis also works synergistically with flexor digitorum profundus and other flexors during various gripping tasks.
Finger movements are often subtle yet complex, relying heavily on the flexor digitorum superficialis. Through its contractions, it enables actions like typing, playing instruments, and performing intricate manual tasks. Knowledge of where this muscle originates and inserts assists individuals in understanding common injuries or conditions, like tendonitis.
Anatomists and healthcare professionals frequently study this muscle’s anatomy. Recognizing its importance not only aids in discussions related to anatomy but also informs treatment plans for hand and forearm injuries. Overall, flexibility and movement articulation attributed to the flexor digitorum superficialis highlight the sophistication of hand mechanics.
Anatomy of Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
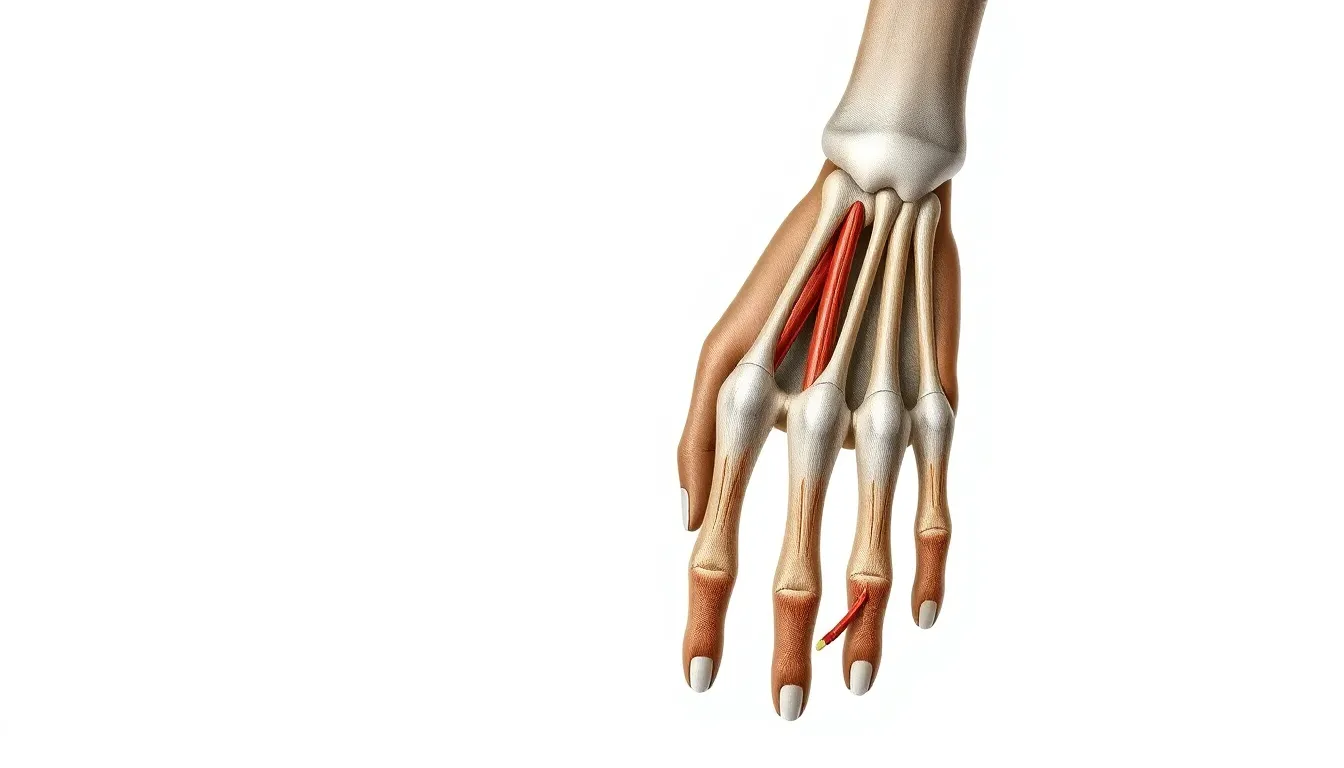
The flexor digitorum superficialis plays a vital role in hand movements. Understanding its origin and insertion provides deeper insight into its function.
Origin of Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
The flexor digitorum superficialis originates from several key structures. It arises from the common flexor tendon attached to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. Muscle fibers also stem from the anterior surface of the ulna and radius, creating a broad base for movement. Each of these origins contributes to the muscle’s strength and versatility. Overall, its origins reflect its essential role in flexing the fingers.
Insertion of Flexor Digitorum Superficialis
Inserting at the middle phalanges of the second to fifth digits, the flexor digitorum superficialis facilitates crucial hand functions. Each tendon splits as it approaches the distal aspect of the fingers, allowing for precise flexion. This anatomical arrangement permits effective flexion at the proximal interphalangeal joints. Such positioning enables the muscle to play a significant role during gripping and manipulation tasks. Overall, its insertion highlights its importance in hand mechanics.
Function and Importance
The flexor digitorum superficialis plays a pivotal role in hand functionality. It facilitates complex finger movements that enable daily activities.
Role in Finger Movement
Flexion of the proximal interphalangeal joints relies heavily on this muscle. It connects to the middle phalanges of the second to fifth digits, allowing for precise bending. During tasks like writing, typing, or playing instruments, the muscle’s actions become crucial. This capability highlights its contribution to fine motor skills. Coordinated movements result from its synergy with other hand muscles, ensuring smooth operation. As it engages, the muscle provides dynamic control over various finger positions.
Contribution to Grip Strength
Grip strength significantly benefits from the flexor digitorum superficialis. By flexing multiple joints simultaneously, it enhances the overall power of the hand. Activities like holding objects or grasping tools depend on its strength. Its broad base of origin permits effective force distribution during gripping tasks. The muscle’s engagement contributes to stable and controlled grasps, necessary for lifting or manipulating objects. These actions underscore the importance of understanding this muscle’s role, especially in preventing injuries and developing rehabilitation strategies.
Clinical Relevance
The flexor digitorum superficialis muscle plays an integral role in various hand functions. Awareness of its clinical significance enhances understanding of related injuries and surgical interventions.
Common Injuries
Tendonitis represents one common injury associated with the flexor digitorum superficialis. Patients may experience pain and swelling in the forearm and wrist due to overuse. Repetitive strain from activities like typing or playing instruments often leads to inflammation. Additionally, acute injuries, such as tendon ruptures, might occur from trauma. Such conditions can result in loss of finger mobility, making daily tasks challenging. Effective management often requires physical therapy or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Recognizing symptoms early allows for timely treatment, preventing long-term complications.
Surgical Considerations
Surgical interventions for injuries involving the flexor digitorum superficialis can be complex. Procedures may involve tendon repair or reconstruction, depending on the severity of the injury. Surgeons often assess the extent of damage through imaging studies before deciding on the approach. Post-surgery, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in restoring function and strength. Physical therapy typically focuses on regaining range of motion and coordination of finger movements. Successful outcomes rely on both surgical precision and adherence to rehabilitation protocols. Understanding anatomical relationships enhances surgical planning and minimizes risks during these procedures.
The flexor digitorum superficialis is a vital muscle that significantly influences hand function. Its unique origin and insertion allow for essential finger movements that enhance daily activities like writing and gripping. Recognizing the muscle’s role not only aids in understanding anatomy but also highlights the importance of preventing injuries. Awareness of potential issues such as tendonitis or acute ruptures can lead to timely intervention and effective rehabilitation strategies. By appreciating this muscle’s contributions to hand mechanics, individuals can better navigate the complexities of hand injuries and their management.